“Discover the 10 must-have Business Analyst skills for 2025 — from communication to data literacy — to future-proof your BA career.”
Introduction: Why 2025 Is the Year to Be a Business Analyst 🚀
If you’re thinking about starting a career as a Business Analyst (BA) or want to upgrade your skills to stay relevant, there’s no better time than 2025
With companies shifting to AI-driven products, Agile delivery, and digital transformation, the demand for sharp, adaptable BAs is at an all-time high. But what really makes a great BA in today’s tech-heavy world?
Let’s break down the 10 core skills you absolutely need — explained simply so even a beginner can follow along
🧩 1. Strong Communication & Storytelling Skills
A BA’s superpower is communication.
You’ll constantly explain complex requirements to stakeholders, developers, and testers.
In 2025, it’s not just about writing emails — it’s about storytelling with data.
👉 Tips to Build This Skill:
- Practice active listening during meetings.
- Use simple, jargon-free language.
- Convert technical requirements into clear stories and visuals.
Future Trend: With hybrid teams and AI-driven collaboration tools (like MS Copilot & Zoom AI), BAs must be comfortable delivering crisp presentations virtually.
📝 2. Requirements Elicitation & Documentation
Think of this as digging for gold.
You need to gather the right requirements from stakeholders and document them clearly so that everyone knows what to build.
👉 Best Practices:
- Conduct workshops & interviews.
- Use user stories, not just plain paragraphs.
- Maintain a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) to avoid gaps.
📊 Diagram Suggestion:
A simple flow chart showing how stakeholder input → BA analysis → documented requirements → development.
📊 3. Analytical Thinking & Problem-Solving
A BA is a detective of business problems.
You’ll analyze data, identify bottlenecks, and propose solutions.
👉 Ways to Improve:
- Practice root-cause analysis using the 5-Whys technique.
- Study process flows (BPMN) to visualize problems.
- Develop a habit of questioning assumptions.
Hero Tip: Pair analytical thinking with critical thinking to suggest innovative solutions, not just surface fixes
🖥️ 4. Data Literacy & Basic SQL
Data is the new gold for BAs in 2025.
You don’t need to be a data scientist, but knowing how to query databases using SQL or create simple reports in Excel or Power BI makes you 10× more effective.
👉 Quick Wins:
- Learn basic SELECT, JOIN, GROUP BY commands.
- Use Excel Pivot Tables to visualize trends.
- Understand KPIs relevant to your domain.
📈 Chart Suggestion:
Embed a sample bar chart comparing sales by region as an example of a KPI dashboard.
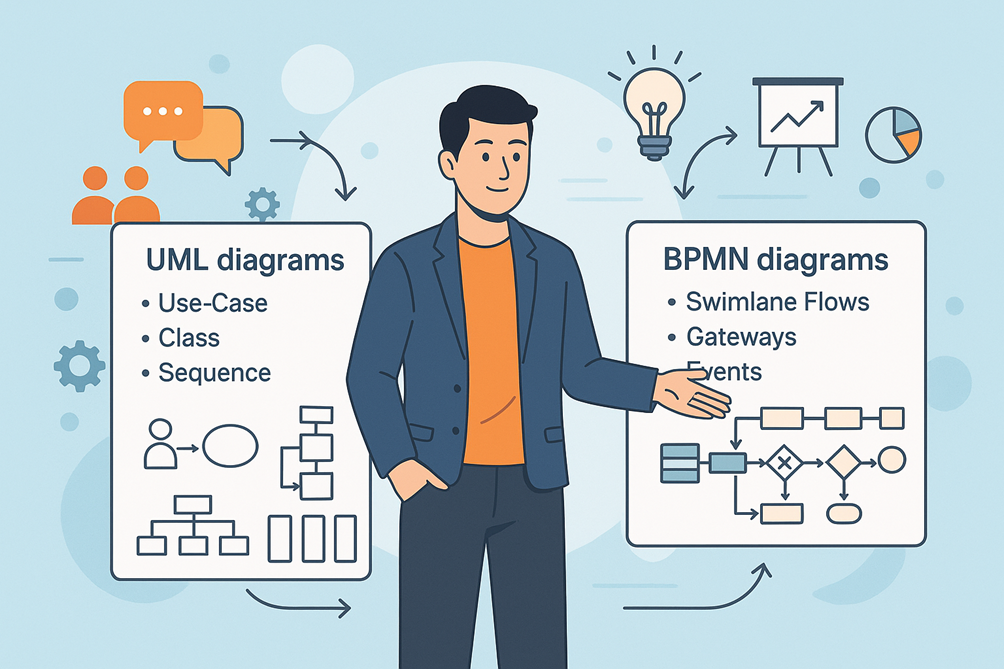
🎨 5. Modelling & Diagramming (UML, BPMN, Wireframes)
Visuals help everyone stay on the same page.
A good BA knows how to create diagrams like use-case diagrams, swimlane BPMN charts, and simple wireframes for apps.
👉 Tools to Try:
- Lucidchart, Draw.io, or Miro for diagrams.
- Balsamiq or Figma for wireframes.
📐 Diagram Suggestion:
Show a sample wireframe of a login page to demonstrate how BAs visualize screens
👥 6. Stakeholder Management & Facilitation
BAs often act as the bridge between business and technology.
You’ll meet stakeholders with different priorities, and your job is to align everyone toward the same goal.
👉 Pro Tips:
- Develop empathy and negotiation skills.
- Keep everyone informed with meeting notes and updates.
- Learn to run workshops effectively — either onsite or virtually.
Future Outlook: Virtual workshops using Miro and MURAL boards will dominate in 2025, so online facilitation skills will be a must.
⚡ 7. Agile & User Story Writing
Most organizations now follow Agile Scrum or Kanban.
You’ll need to write Epics, User Stories, and Acceptance Criteria that developers can act on.
👉 Checklist for Great User Stories:
- Follow the INVEST principle (Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Small, Testable).
- Include clear acceptance criteria.
- Link stories to business value.
📊 Chart Suggestion:
Include a burndown chart example to show how Agile teams track progress
💻 8. Familiarity with BA/PM Tools
In 2025, tool knowledge is no longer optional.
You must be able to work with:
- Jira and Confluence for Agile tracking
- MS Excel & Power BI for reporting
- Miro & Lucidchart for diagrams
- Zapier/Power Automate for simple integrations
Pro Tip: Start by mastering Jira’s Backlog, Sprint Board, and Reports.
📈 9. Domain Knowledge in Your Industry
Whether it’s Wealth Management, Payments, eCommerce, or Healthcare, understanding the business processes, compliance needs, and customer pain points will set you apart from other BAs.
👉 Example:
A BA in Wealth Management must know about KYC, AUM, investment suitability, and compliance regulations.
📘 Static Information Box:
“BAs with niche domain expertise earn up to 25% higher salaries than generalists.”
🚀 10. Continuous Learning & Adaptability
The tech landscape changes every 6 months.
A future-proof BA never stops learning.
👉 Ways to Stay Relevant:
- Take certifications like ECBA, CCBA, or CSM.
- Follow AI trends and Generative AI tools that are reshaping business workflows.
- Practice lifelong learning with podcasts, blogs, and LinkedIn Learning.
Future Trend: By 2026, AI copilots will help draft BRDs and RTMs, so adaptability to new tools is critical.
🌟 Summary Table: Top 10 BA Skills for 2025
| # | Skill | Why It Matters in 2025 |
| 1 | Communication & Storytelling | Explains complex ideas simply |
| 2 | Requirements Elicitation | Prevents costly re-work |
| 3 | Analytical Thinking | Solves business problems effectively |
| 4 | Data Literacy & SQL | Enables data-driven decisions |
| 5 | Modelling & Wireframes | Improves collaboration and clarity |
| 6 | Stakeholder Management | Aligns diverse interests |
| 7 | Agile & User Stories | Speeds up product delivery |
| 8 | BA Tools (Jira, Miro, Power BI) | Boosts productivity |
| 9 | Domain Knowledge | Adds niche value |
| 10 | Continuous Learning | Future-proofs your BA career |
🏆 Conclusion: Your BA Journey Starts Now
Becoming a skilled BA in 2025 is not just about technical know-how — it’s about being curious, adaptable, and people-oriented.
Start by mastering 2–3 of these skills today and gradually build the rest.
Remember: A BA who can communicate clearly, understand data, and bridge business with tech will always be in demand.
💡 Call to Action:
Share this blog with your friends or colleagues who are exploring a BA career, and comment below on which skill you’ll focus on first!