Learn the 7 phases of the product lifecycle — from ideation to sunset. A complete guide for new product managers to plan, scale, and sustain successful products
🌟 Introduction: Why Every Product Manager Must Know the Product Lifecycle
Imagine launching a brilliant product idea — it gains traction, users love it, and revenue soars.
But over time, growth slows down, competition rises, and suddenly the same product feels outdated.
That’s the Product Lifecycle (PLC) in action — a natural progression every product goes through, from introduction to decline.
For new Product Managers (PMs), understanding this lifecycle is essential. It helps you forecast demand, plan launches, allocate resources wisely, and most importantly, extend the profitable life of your product.
Let’s dive into the 7 Phases of the Product Lifecycle, with real examples, visuals, and strategies to help you master each one.
🔍 What Is the Product Lifecycle?
The Product Lifecycle describes the stages a product passes through from its conception to its discontinuation.
It’s like the product’s biography — from the idea’s birth to its eventual retirement. The classic model includes four phases — Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline —
but modern PMs expand it to seven distinct stages, adding key early and late steps like Ideation, Development, and Sunset/Retirement
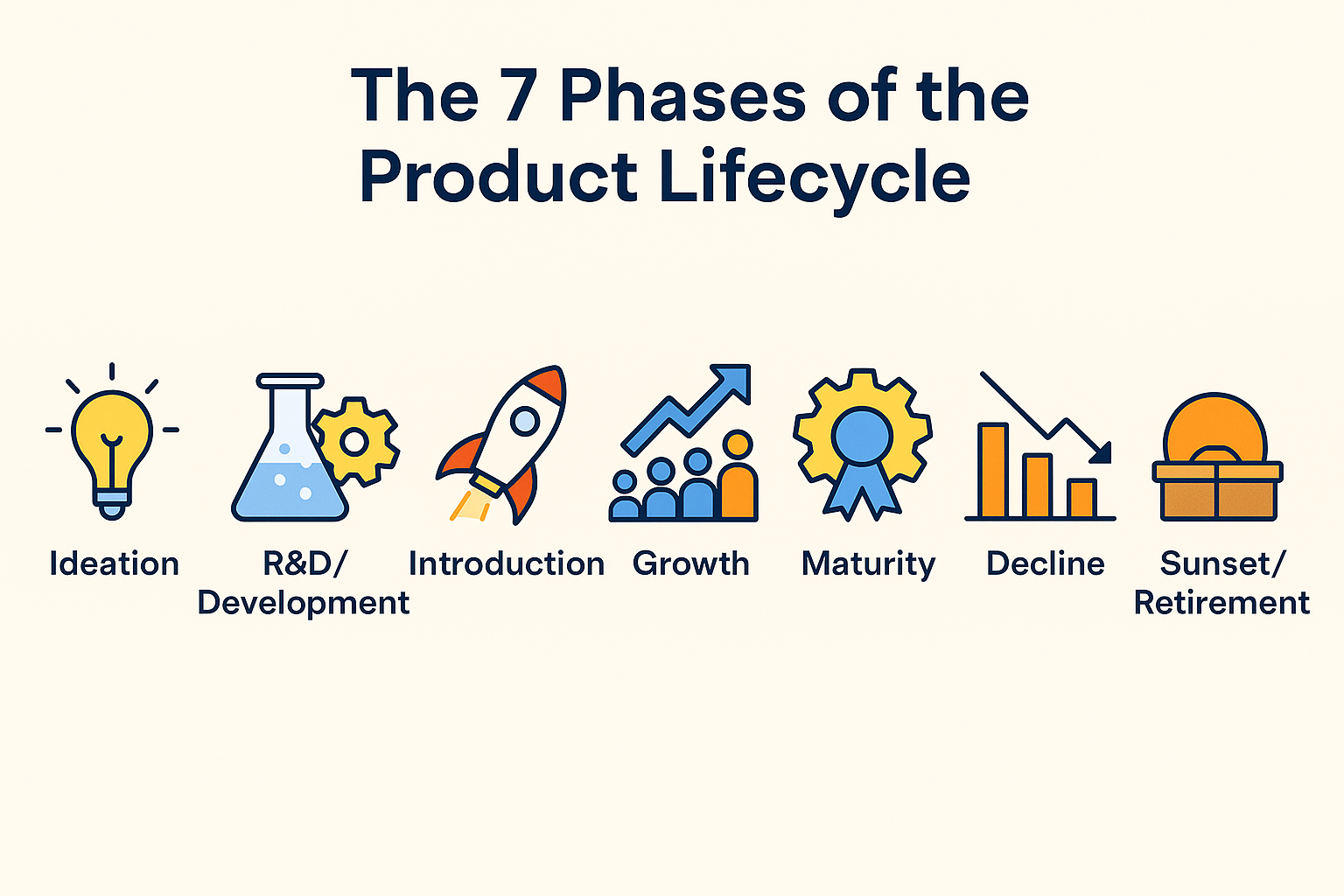
🧭 The 7 Phases of the Product Lifecycle
Let’s go step-by-step through each stage:
1️⃣ Ideation — Finding the Spark
Definition:
Ideation is the creative phase where new product ideas are generated, inspired by customer pain points, market trends, or technology innovations.
Activities in This Phase:
- Brainstorming sessions and design thinking workshops
- Market and competitor analysis
- Customer interviews to uncover unmet needs
Example:
Airbnb’s founders noticed travellers struggling to find affordable lodging and created a solution connecting homeowners with guests.
Benefits:
- Early validation prevents costly mistakes
- Promotes innovation and creativity
- Sets a clear problem-solution fit

2️⃣ Research & Development (R&D) — Building the Foundation
Definition:
Once an idea is shortlisted, it moves into research and development, where feasibility, cost, and user requirements are validated.
Key Activities:
- Creating prototypes or MVPs (Minimum Viable Products)
- Conducting usability tests
- Estimating production or development costs
- Defining key features and technology stack
Example:
Before launching, Apple conducts extensive prototyping of new iPhone features through internal R&D.
Benefits:
- Reduces launch risk
- Builds confidence through early testing
- Helps secure investor or stakeholder buy-in

3️⃣ Introduction — Launch and Market Entry
Definition:
This is where the product officially enters the market. The focus shifts from development to marketing, positioning, and user onboarding.
Key Goals:
- Create awareness and educate users
- Build initial trust and credibility
- Establish a product-market fit (PMF)
Challenges:
- High costs and low revenue
- Slow adoption curve
- Need for strong marketing push
Example:
When Netflix launched streaming in 2007, awareness was low. Their focus was on educating DVD customers to switch to digital streaming.
Benefits:
- First-mover advantage if well-timed
- Brand differentiation
- Early adopter loyalty

4️⃣ Growth — Scaling and Market Expansion
Definition:
Growth begins when early adopters turn into mainstream users. Sales increase, the product gains recognition, and new features are added.
Key Activities:
- Optimize customer acquisition funnels
- Improve onboarding and retention
- Expand distribution channels
- Hire more teams (sales, support, dev)
Example:
Zoom saw massive growth during the pandemic as demand for remote collaboration surged.
Benefits:
- Rapid revenue increase
- Market leadership opportunity
- Potential for partnerships or funding

5️⃣ Maturity — Optimization and Saturation
Definition:
The maturity phase marks the peak of the product’s success. Sales stabilize, market share is maximized, and competition intensifies.
Key Activities:
- Product differentiation and brand loyalty programs
- Cost optimization and process efficiency
- Exploring new customer segments
Example:
Facebook reached maturity when global user growth slowed, and focus shifted to monetization (ads, business tools, reels).
Benefits:
- Stable profits
- Economies of scale
- Strong brand recognition

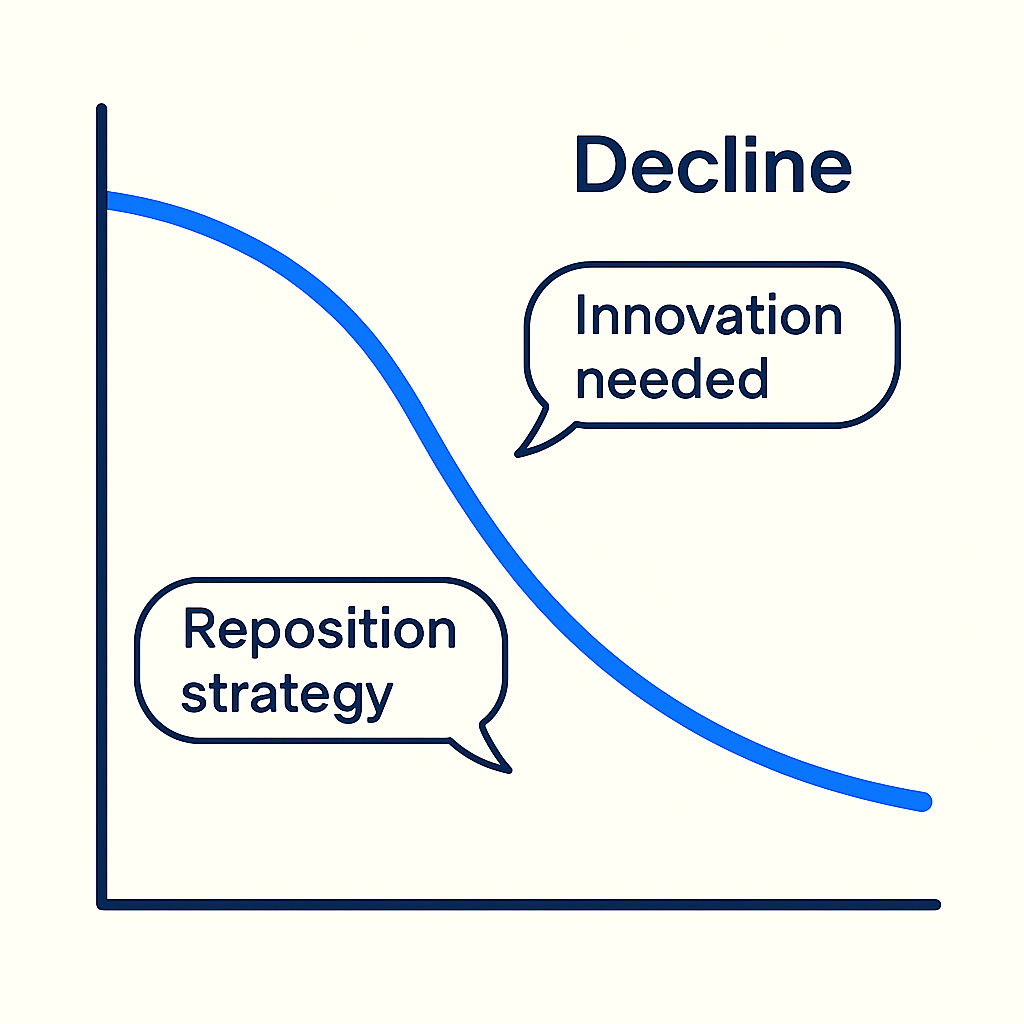
6️⃣ Saturation & Decline — Navigating Slowdown
Definition:
As newer competitors enter or customer preferences evolve, the product’s growth slows or begins to decline.
Key Signs:
- Reduced engagement or sales
- Market saturation
- Rising customer acquisition costs (CAC)
Example:
Nokia dominated the mobile market but declined when smartphones disrupted their product line.
PM’s Response:
- Rebrand or reposition the product
- Introduce new features or redesign UX
- Explore emerging markets or niches
7️⃣ Sunset / Retirement — The End-of-Life Strategy
Definition:
Eventually, every product reaches a stage where it’s no longer viable to maintain or support. That’s where the sunset phase begins.
Key Actions:
- Communicate clear end-of-support plans
- Migrate customers to newer versions
- Archive or repurpose technology
Example:
Google often sunsets older apps (like Google Hangouts) and merges features into new ones (Google Chat).
Benefits:
- Frees resources for innovation
- Maintains brand reputation
- Allows smooth transition for users

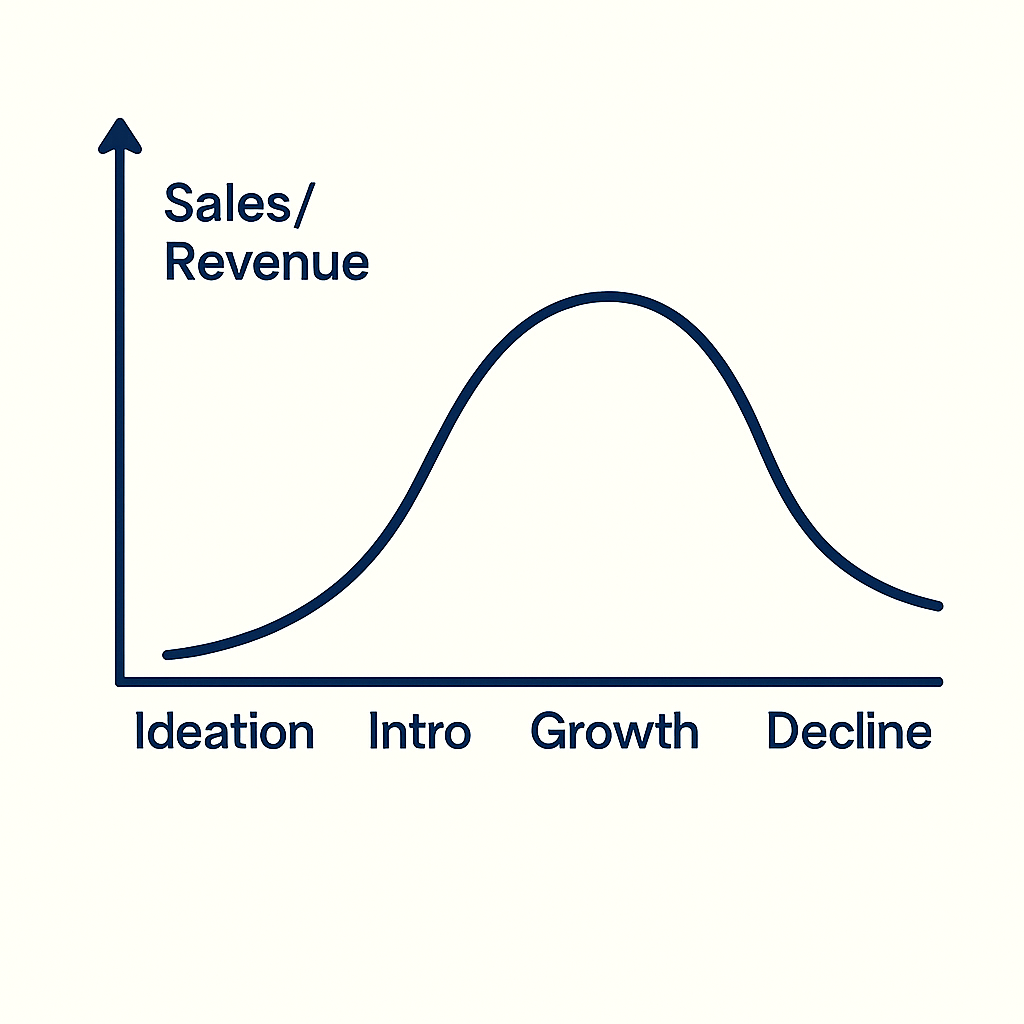
⚙️ Product Lifecycle Diagram
You can visualize the 7 phases as a curve showing market growth over time
💡 Benefits of Understanding the Product Lifecycle
For a Product Manager, mastering the PLC unlocks several strategic advantages:
- Better Forecasting:
Predict market trends and plan inventory or feature roadmaps. - Optimized Budgeting:
Know where to invest — marketing during introduction, innovation during maturity, cost-cutting during decline. - Smarter Roadmaps:
Align product updates with the lifecycle stage to maximize ROI. - Customer-Centric Strategy:
Tailor communication and pricing based on customer maturity. - Competitive Edge:
Anticipate decline early and pivot before rivals do.
🌍 Real-World Examples
| Company | Product | Stage | Strategy |
| Apple | iPhone | Maturity | Incremental innovation, loyalty programs |
| Netflix | Streaming | Growth | Global expansion, original content |
| Hangouts | Sunset | Migrated users to Google Chat | |
| Tesla | Cybertruck | Introduction | Preorders and hype marketing |
🔮 Future Trends in Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
Modern Product Management is evolving with data-driven and AI-assisted lifecycle tools. Here’s what’s next:
1. AI-Powered Forecasting
Tools like Jira Product Discovery and Aha! now use machine learning to predict lifecycle shifts and automate backlog prioritization.
2. Sustainable Product Lifecycles
Green PLM is emerging — companies design for reuse, recyclability, and energy efficiency across the lifecycle.
3. Continuous Innovation Loops
Instead of ending in decline, modern digital products follow continuous lifecycle loops — frequent updates, feedback cycles, and SaaS renewals keep products evergreen.
4. Cross-Functional Lifecycle Teams
PMs now collaborate more closely with marketing, UX, and data science teams to monitor product health metrics in real time
🧭 Summary Table: The 7 Phases at a Glance
| Phase | Goal | Key Focus | Example |
| Ideation | Generate ideas | Identify user needs | Airbnb idea stage |
| R&D | Validate & prototype | MVP & testing | Apple R&D labs |
| Introduction | Launch | Awareness & PMF | Netflix streaming launch |
| Growth | Scale | Acquisition & retention | Zoom surge |
| Maturity | Optimize | Loyalty & efficiency | Facebook ads model |
| Decline | Reposition | Innovation or cost control | Nokia |
| Sunset | Retire | Transition & resource shift | Google Hangouts |
🧩 Conclusion: Think Like a Product’s Lifelong Guardian
As a new Product Manager, your role isn’t just to launch — it’s to nurture, grow, and evolve your product through each lifecycle stage.
The market will change, user needs will shift, but products that are continuously monitored and innovated can stay relevant for decades.
“Products don’t fail because they die — they fail because PMs stop evolving them.”
Keep your roadmap agile, track lifecycle metrics (engagement, churn, feature adoption), and remember — every phase is an opportunity to innovate.